The following is an introduction to laser rangefinders for the power industry:
Functional features
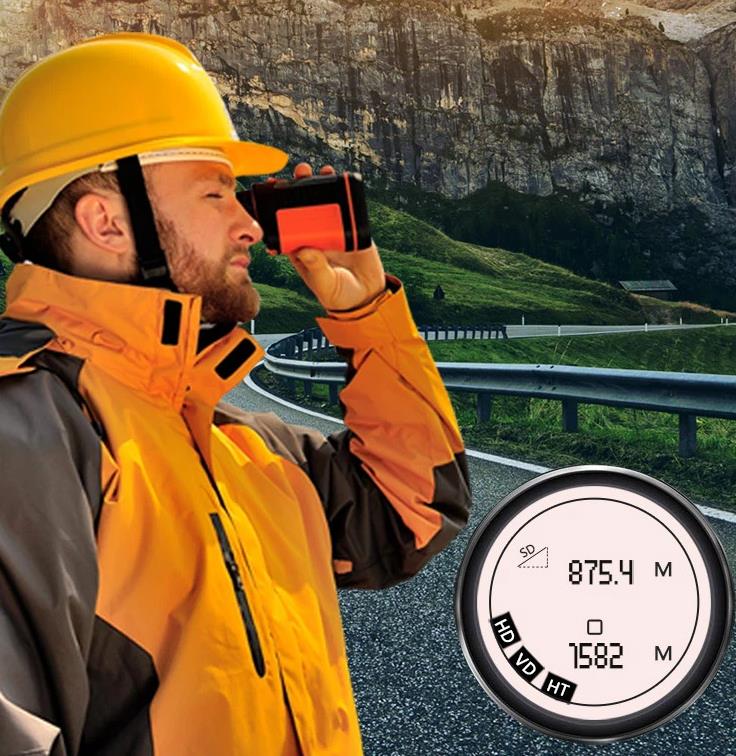
Accurate distance measurement: It can accurately measure the distance between power facilities, such as the interval between poles and towers, and the length of wires. The measurement accuracy can usually reach meters or even centimeters, providing accurate data support for the planning, construction and maintenance of power lines.
Angle measurement: Some laser rangefinders are equipped with angle sensors that can measure horizontal and vertical angles, thereby measuring the cross-span distance, vertical distance and clearance distance of overhead power lines, which helps to evaluate the safety and compliance of the lines.
Multi-function integration: In addition to the distance measurement and angle measurement functions, it may also integrate height measurement, speed measurement, temperature measurement, GPS positioning and other functions to obtain more information related to power facilities, such as pole tower height, conductor temperature, equipment location, etc., so that power workers can fully understand the operation status of the power system.
Data display and storage: It has a clear liquid crystal display (LCD) that can display measurement data in real time and store a large number of measurement results, which is convenient for staff to consult and analyze later. Some also support data transmission functions, which can upload data to computers or other devices for further processing.
Portability: The design is light and compact, which is convenient for power workers to carry to various power construction sites. Whether it is in mountainous areas, wild areas or urban power facility maintenance work, it can be easily operated to improve work efficiency.
Working principle
The working principle of the laser rangefinder telescope is based on the propagation and reflection of lasers. The instrument emits a laser pulse to the target, and then measures the time from the laser emission to the laser being reflected back by the target and received by the instrument. According to the speed of light in the air, the distance between the instrument and the target is calculated by the formula
d=c×t/2 (where d is the distance, c is the speed of light, and t is the time).

Application scenario
Power line planning and design: In the planning stage of new power line construction, the use of laser rangefinder telescopes can accurately measure the length of the route, terrain undulations, and the distance across obstacles, etc., to help engineers design reasonable line directions and tower layouts, optimize the design of power lines, and reduce construction costs.
Installation and commissioning of power facilities: During the installation of power equipment, such as the assembly of iron towers, the erection of electric poles, and the installation of electric wires, it is necessary to accurately measure the distance and height between the equipment to ensure that the installation position is accurate and the normal operation of the power system is guaranteed.
Power line inspection and maintenance: Power inspectors can use laser ranging telescopes to regularly inspect power lines, measure the distance changes between power facilities such as electric poles and transformers, check whether the sag of power lines and the cross-span distance meet safety standards, and promptly discover potential safety hazards, such as line aging and tower tilt, so as to take corresponding maintenance measures.
Emergency repair: When the power system fails or suffers from natural disasters, the laser ranging telescope can help repair personnel quickly measure the relevant data of the damaged power facilities, evaluate the fault situation, formulate repair plans, improve repair efficiency, and restore power supply as soon as possible.

Selection points
Measurement range: Select a laser ranging telescope with a suitable measurement range according to actual work needs. The measurement range used in the general power industry ranges from hundreds of meters to thousands of meters.
Measurement accuracy: The higher the accuracy requirement, the better. Usually, the accuracy needs to reach ±1m or even higher to meet the strict requirements of power engineering for the accuracy of measurement data.
Telescope magnification: A higher magnification can observe the target more clearly, but the actual use scenario and stability must also be considered. Generally, the magnification of 7x-10x is more common.
Laser safety level: Class 1 laser safety level products should be selected to ensure harmlessness to the human eye and the safety of operators.
Environmental adaptability: The power working environment is complex and diverse. It is necessary to select a laser ranging telescope with waterproof, dustproof, shockproof and other functions to adapt to various harsh natural environments and ensure the normal operation and service life of the instrument.