With the development of thermal imaging technology, infrared thermal imagers have been successfully used in security monitoring. In some complex monitoring scenes, it has more obvious advantages than general infrared monitoring equipment. Taking advantage of the infrared thermal imager's ability to search for targets over a long distance and over a large area, this application greatly meets the long-distance and large-scale monitoring and detection requirements of night vision monitoring in the security industry. So, what is the working principle of infrared thermal imagers in security monitoring?
The working principle of infrared thermal imagers is that it does not require the assistance of external light sources, but instead receives infrared radiation (related to the temperature of the object itself) generated by the object, that is, captures the temperature of the object to form an image. Although infrared radiation (IR) cannot be observed by the naked eye, infrared thermal imagers can convert it into visible light images to depict the temperature changes of the measured object or scene. Any object with temperature will emit infrared rays, and the higher the temperature of the object, the greater the amount of infrared radiation. The thermal imager receives the infrared rays emitted by the object, displays the temperature distribution on the surface of the measured object through a colored picture, and finds the abnormal temperature points based on the slight difference in temperature, thereby playing a role in maintenance. It is also generally called an infrared thermal imager.
At its core is the thermal imager, a sensor that detects very small temperature differences and converts them into real-time video images. However, only the thermal outlines of people and objects can be seen, not the true appearance of the objects.
The infrared energy emitted by an object is focused on the infrared detector through an optical lens, and the detector sends information to the sensor electronics for image processing, which translates the data sent by the detector into an image that can be viewed in the viewfinder or on a standard video monitor or LCD screen.
Infrared thermal imaging is a technology that converts infrared images into thermal radiation images, which can read temperature values from the image. Therefore, each pixel in the thermal radiation image is actually a temperature measurement, which can achieve non-contact measurement of the surface temperature of the object.
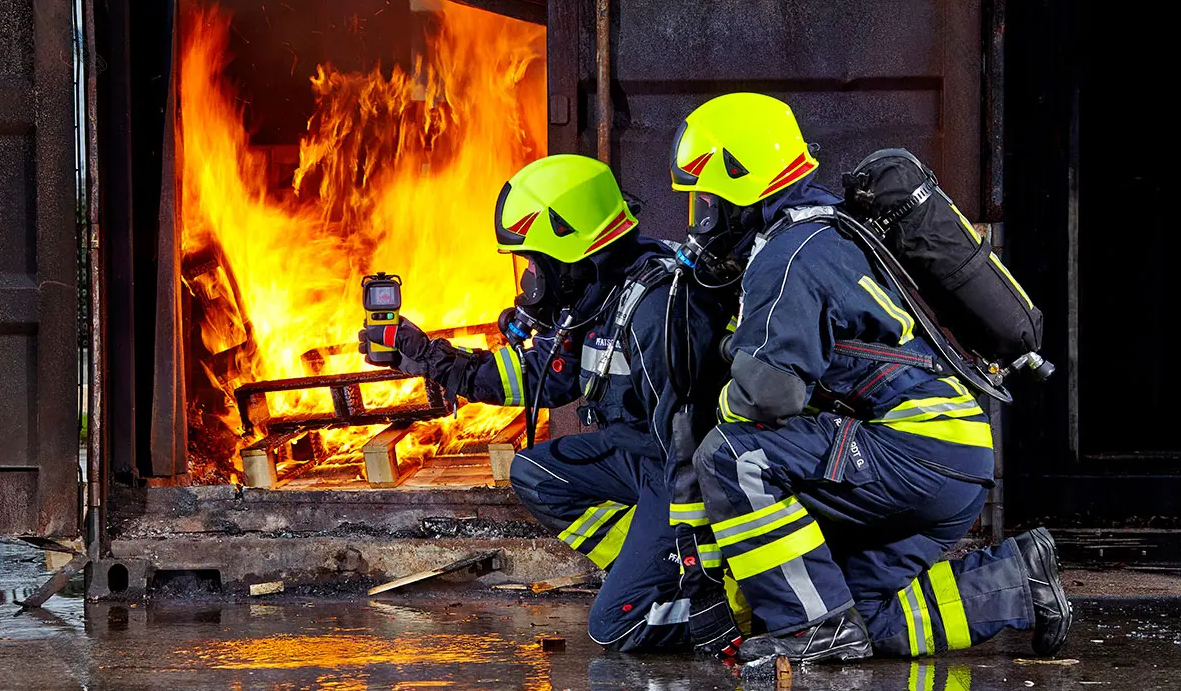

The construction of an infrared thermal imager is similar to that of a digital video camera. The main components include a lens to focus the infrared radiation on the detector, and software and electronics to process and display the thermal signal and thermal image.
Working principle:
Natural light is composed of light waves with different wavelengths. The visible range of human eyes is roughly 390-780nm. Electromagnetic waves shorter than 390nm and longer than 780nm cannot be felt by human eyes. Among them, electromagnetic waves with wavelengths less than 390nm are located outside the purple of the visible light spectrum, called ultraviolet rays; electromagnetic waves longer than 780nm are located outside the red of the visible light spectrum, called infrared rays, and their bands range from 780nm to 1mm.
Advantages of thermal imaging monitoring:
Infrared thermal imager structure_Infrared thermal imager working principle_Infrared thermal imager principle
1. Target monitoring at night and in severe weather conditions.
There is no sunlight in the night environment, and you can't see your fingers. The dim light of street lights is vaguely visible. In addition, many targets are not illuminated by street lights at all, making it even more difficult to see the target clearly. If an infrared thermal imager is used, the visual difficulties brought by the night can be overcome. The working principle is to automatically receive the infrared thermal radiation emitted by the target being measured, especially in severe weather conditions, and various targets, personnel, vehicles, etc. can still be monitored.

2. Fire prevention monitoring. The biggest function of infrared thermal imagers is to measure the target temperature. Therefore, when a fire occurs, it can quickly find the exact location of the fire by receiving infrared thermal radiation. Even in the vast smoke, infrared thermal imagers can penetrate layers of smoke to find the fire point and help put out the fire in time.
3. Identification of camouflage and hidden targets.
When the police need to track some targets during case investigations, these fugitives often hide in the grass and woods, and it is difficult to find them with the help of visual obstacles. Infrared thermal imagers can come in handy at this time. By monitoring the human body temperature that is higher than the ambient temperature, the target traces will no longer be hidden, greatly reducing the search labor cost and saving search time.
Being good at using the working principle of infrared thermal imagers will only help the security work. The reason why infrared thermal imagers have become a good partner for people's security work is that they are like a talking machine, continuously recording the target temperature data, generating images for relevant personnel to analyze, and can immediately find the target for accurate monitoring when needed.