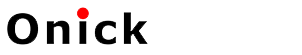Infrared thermal imager is a new type of advanced infrared imaging instrument, which has a wide range of applications in military and civilian industries and shows fast, non-contact characteristics.
1. What is a thermal imager?
A thermal imager is a special camera equipped with a sensor that detects thermal energy and converts it into visible light. This means that when you look at an object, you see different energy emissions of the object. The more thermal energy an object emits, the brighter it will be on the image. Conversely, the less heat, the darker it is.
2. Can it be imaged through walls?
No, a thermal imager cannot see through walls, but it can see its heat distribution through the heat generated on the wall, which is suitable for detecting floor heating and floor heat. It can also see through fog, thick smoke or even completely in the dark. This means that it can provide you with accurate heat temperatures, even when there is almost no available light.
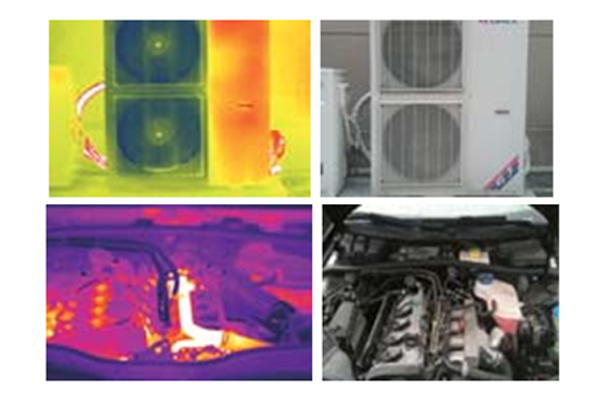
3. How do thermal imagers make daily life safer?
First of all, detect house quality defects. During the construction process, if you don't pay much attention, it will cause some defects and damage to the building. If you fail to take relevant remedial measures in time, it will cause significant impacts and losses. The application of infrared thermal imagers can quickly and effectively find out the causes, defect locations and other factors, so that the staff can deal with them in time to avoid these housing quality problems affecting their bearing capacity and durability, causing some accidents and adversely affecting the personal safety of our citizens.
Secondly, the detection of leakage. If the building is exposed to wind and rain for many years, it is easy to have cracks, breaks and water penetration in the wall, which will adversely affect the structure of the house. In severe cases, it will also affect and damage human health. At this time, the infrared thermal imager can conduct a full range of detection and analysis, so that everyone can find the precise location and potential problems, and do relevant treatment in time to improve the quality of the building and avoid adverse effects.
4. Can thermal imagers detect diseases?
Infrared thermal imager detection is a passive method and does not produce any radiation or other substances that are harmful to the human body. When infrared thermal imagers detect patients, they can only detect diseases with temperature changes that are fed back to the human body surface, and other diseases cannot be seen. For example, if some internal organs are lesioned, the surface temperature of the human body at the corresponding position will be abnormal. This disease can be detected by thermal imagers as a rough check.
5. How do thermal cameras work?
Thermal imagers have a special lens on them that uses sensors to see the thermal radiation from all the different light sources in its view. The lens will use the heat detector to produce a temperature image, a process that is very fast - lasting one second. In such a short time, information from thousands of detailed points is collected and processed. The thermal analysis map is then converted into a thermal image that is finally displayed on the display screen.
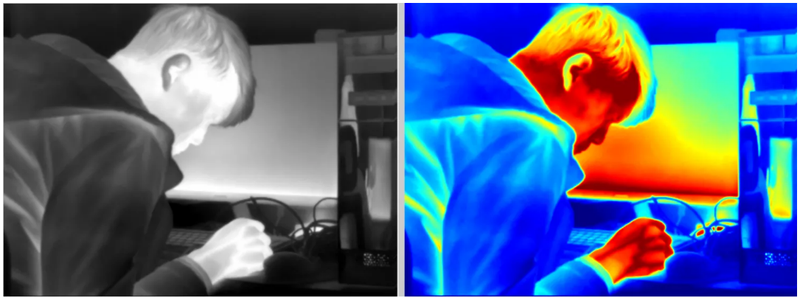
6. How accurate is a thermal imager?
This usually depends on the specifications and design of the thermal imager. The most important factors for this are the frame rate and whether it is an uncooled or cooled thermal imager. However, most, including all Nidu thermal imagers, will have a slight variation of 0.2℃.
7. What is the resolution of thermal imaging?
Thermal resolution determines how clear the thermal image appears on the camera. The higher this number, the clearer the details. Usually, the resolution is measured in pixels - given as a number x number (e.g. 384x288). The first number indicates the horizontal clarity and the second number indicates the vertical clarity.