Night vision devices mainly help users observe targets in the dark by enhancing or converting weak light or infrared radiation. They are mainly divided into the following categories. Their working principles and applicable scenarios are as follows
1. Low-light night vision devices (Image Intensifier Tubes, IIT)
Principle:
The weak ambient light (moonlight, starlight, etc.) is converted into electrons through the photocathode. After multiplication, the electrons bombard the fluorescent screen to generate a visible enhanced image (usually green, because the human eye is most sensitive to green).
Features:
Depends on ambient light and is ineffective in a completely dark environment.
The image is clear and has high resolution, but it is easily damaged under strong light.
Typical uses: military night combat, night reconnaissance, wildlife observation.
Generational technology:
Generation (Gen 1): basic enhancement, obvious edge distortion.
Generation (Gen 2): Add microchannel plate (MCP) for better enhancement.
Generation 3+/Gen 4: higher sensitivity, longer life, military grade.
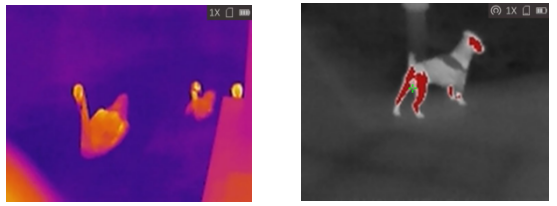
2. Thermal Imager
Principle:
Detects infrared radiation (heat) emitted by the target object, and different temperatures are displayed in different colors (such as white/red for high temperature and black/blue for low temperature).
Features:
Completely independent of light, can penetrate smoke and mist.
Can detect hidden targets (such as animals or humans hiding in the grass).
Typical uses: fire rescue, military sniping, building heat leak detection.
Technology type:
Non-cooling type: low cost, slow response (mainly for civilian use).
Cooling type: high sensitivity, used for military or scientific research.
3. Active Infrared Night Vision Device (Active IR)
Principle:
Emit an infrared beam to illuminate the target, and form an image by receiving the reflected infrared light (need to cooperate with an infrared light source).
Features:
Used in complete darkness, but may be discovered by other infrared devices.
The imaging distance is limited and it is easy to expose itself (has been gradually eliminated in the military).
Typical uses: early military equipment, security monitoring.
4. Digital Night Vision
Principle:
Use high-sensitivity CMOS/CCD sensors to capture weak light, enhance the image through digital signal processing, and output it to the screen or storage.
Features:
Environmental adaptability is strong, and some models can switch between low-light/infrared modes.
Low cost, but latency and noise may be high.
Typical uses: civilian hunting, outdoor adventures.
How to find hidden targets?
Low-light type: relies on ambient light reflected by the target, suitable for open environments without obstructions.
Thermal imaging: identifies targets by temperature difference (such as human body vs cold background), ignoring leaves and smoke obstructions.
Active infrared: requires the target to reflect infrared light, and has poor concealment.
Selection suggestions
Military/law enforcement: thermal imaging or three-generation or higher low-light devices.
Civilian/outdoor: digital night vision devices or low-cost low-light devices.
Completely dark environment: thermal imaging or active infrared must be selected.